这个算法更加注重俄罗斯方块的不死性,如果用遗传算法或者模拟退火算法训练好权重后能够达到很好的效果。主要参考https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41882147/article/details/80005763进行设计。
评价函数
- landingHeight:指当前板块放置之后,板块重心距离游戏区域底部的距离。(也就是小方块的海拔高度)
- erodedPieceCellsMetric:这是消除参数的体现,他代表的是消除的行数与当前摆放的板块中被消除的小方块的格数的成绩。
- boardRowTransitions:对于每一行小方格,从左往右看,从无小方格到有小方格是一种“变换”,从有小方格到无小方格也是一种“变换”,这个属性是各行中“变换”之和
- boardColTransitions:这是每一列的变换次数之和
- boardBuriedHoles:各列中的“空洞的小方格数之和”
- boardWells:各列中“井”的深度的连加和。“井”的定义是,两边(包括边界)都有方块填充的空列。
这里用到的权重如下
| 参数名 | 权值 |
|---|---|
| landingHeight | -4.500158825082766 |
| erodedPieceCellsMetric | 3.4181268101392694 |
| boardRowTransitions | -3.2178882868487753 |
| boardColTransitions | -9.348695305445199 |
| boardBuriedHoles | -7.899265427351652 |
| boardWells | -3.3855972247263626 |
实现思路
主要是像上篇文章所讲的一样,将方块的动作进行重组,以落下一次作为一个组合动作(像格斗游戏里的组合技),不区分方块类型总共可以有40个组合动作,即分别从0-9列下降,旋转0-3次。
然后在操作之前先模拟操作,模拟完这40个动作之后,看看哪个动作得分最高就选哪个进行实操。
# 单一动作下落代码
def frame_step(self,input,dummy=False):
pygame.event.pump()
self.movingLeft = False
self.movingRight = False
# time.sleep(0.2)
terminal = False
landed = False
#none is 10000, left is 01000, right is 00100, space(rotate) is 00010, down is 00001
if self.fallingPiece == None:
# No falling piece in play, so start a new piece at the top
self.fallingPiece = self.nextPiece
self.nextPiece = self.getNewPiece()
self.lastFallTime = time.time() # reset self.lastFallTime
if not self.isValidPosition():
image_data = pygame.surfarray.array3d(pygame.display.get_surface())
# cv2.imshow("name",image_data)
# time.sleep(5)
terminal = True
self.reinit()
return image_data, landed, terminal # can't fit a new piece on the self.board, so game over
# move left
if (input[1] == 1) and self.isValidPosition(adjX=-1):
self.fallingPiece['x'] -= 1
self.movingLeft = True
self.movingRight = False
self.lastMoveSidewaysTime = time.time()
# move right
elif (input[2] == 1) and self.isValidPosition(adjX=1):
self.fallingPiece['x'] += 1
self.movingRight = True
self.movingLeft = False
self.lastMoveSidewaysTime = time.time()
# rotating the piece (if there is room to rotate)
elif (input[3] == 1):
self.fallingPiece['rotation'] = (self.fallingPiece['rotation'] + 1) % len(PIECES[self.fallingPiece['shape']])
if not self.isValidPosition():
self.fallingPiece['rotation'] = (self.fallingPiece['rotation'] - 1) % len(PIECES[self.fallingPiece['shape']])
# move the current piece all the way down
elif (input[4] == 1):
self.movingDown = False
self.movingLeft = False
self.movingRight = False
for i in range(1, BOARDHEIGHT):
if not self.isValidPosition(adjY=i):
break
self.fallingPiece['y'] += i - 1
if self.movingDown:
self.fallingPiece['y'] += 1
self.lastMoveDownTime = time.time()
# let the piece fall if it is time to fall
# see if the piece has landed
cleared = 0
if not self.isValidPosition(adjY=1):
# falling piece has landed, set it on the self.board
landed=True
self.lh = BOARDHEIGHT - self.fallingPiece['y'] - self.getmid()
self.addToBoard()
self.epcm = self.getEpcm()
cleared = self.removeCompleteLines()
self.epcm *= cleared
if cleared > 0:
if cleared == 1:
self.score += 40 * self.level
elif cleared == 2:
self.score += 100 * self.level
elif cleared == 3:
self.score += 300 * self.level
elif cleared == 4:
self.score += 1200 * self.level
self.brt = self.getBrt()
self.bct = self.getBct()
self.holes = self.getHoles()
self.wells = self.getWells()
self.score += self.fallingPiece['y']
self.lines += cleared
self.total_lines += cleared
self.height = self.getHeight()
self.level, self.fallFreq = self.calculateLevelAndFallFreq()
self.fallingPiece = None
else:
# piece did not land, just move the piece down
self.fallingPiece['y'] += 1
if dummy:
return None,landed,terminal
# drawing everything on the screen
DISPLAYSURF.fill(BGCOLOR)
self.drawBoard()
self.drawStatus()
self.drawNextPiece()
if self.fallingPiece != None:
self.drawPiece(self.fallingPiece)
else:
self.drawPiece(self.nextPiece)
pygame.display.update()
image_data = pygame.surfarray.array3d(pygame.display.get_surface())
return image_data,landed, terminal
这个代码里面有单一动作下落,dummy==True的时候就会不更新pygame显示的画面,也就是用于模拟下落。
主函数
主函数的设计如下,主要就是尝试调用恢复。
import sys
sys.path.append("game/")
import tetris_fun_nice as game
import numpy as np
import copy
ACTION= 40
def playGame():
tetris = game.GameState()
action0 = np.zeros(ACTION) # do nothing'
action0[0] = 1
observation0, reward0, terminal = tetris.combine_step(action0)
lobservation = observation0
lscore=0
i = 0
while True:
maxid = 0
maxr = -1000
for j in range(ACTION):
action0 = np.zeros(ACTION)
action0[j] = 1
ttt = copy.deepcopy(tetris)
nextObservation, reward, terminal = ttt.combine_step(action0,True)
if reward > maxr:
maxr = reward
maxid = j
action0 = np.zeros(ACTION)
action0[maxid] = 1
nextObservation, reward, terminal = tetris.combine_step(action0)
if terminal:
print("得分为",lscore)
lscore=tetris.score
lobservation=nextObservation
# print("maxaction=%s,reward=%s"%(maxid, reward))
i += 1
playGame()
最后结果
用这个评价函数得到的结果表现异常的卓越。看下面的图就知道了分数。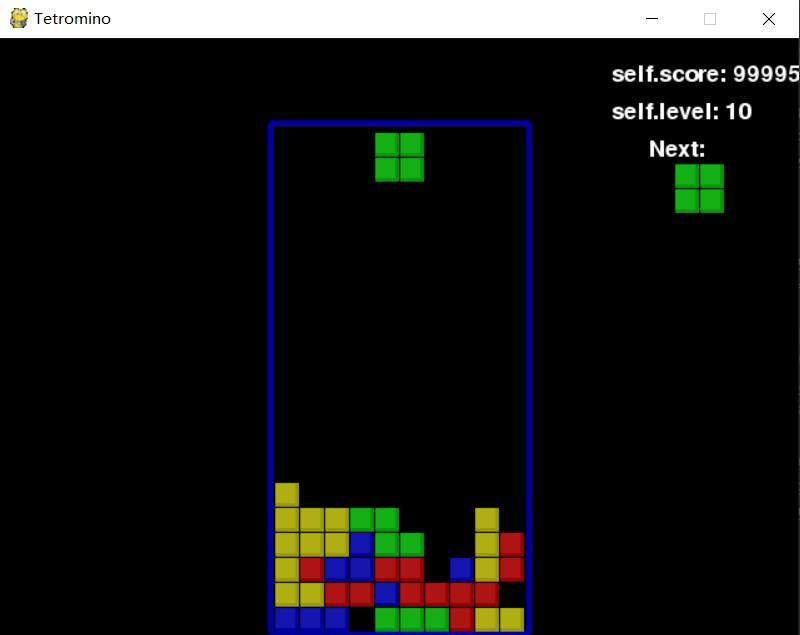
我也不知道他能拿多少,只知道它玩的停不下来。